Contact Us
Contact Us
09 Apr 2024
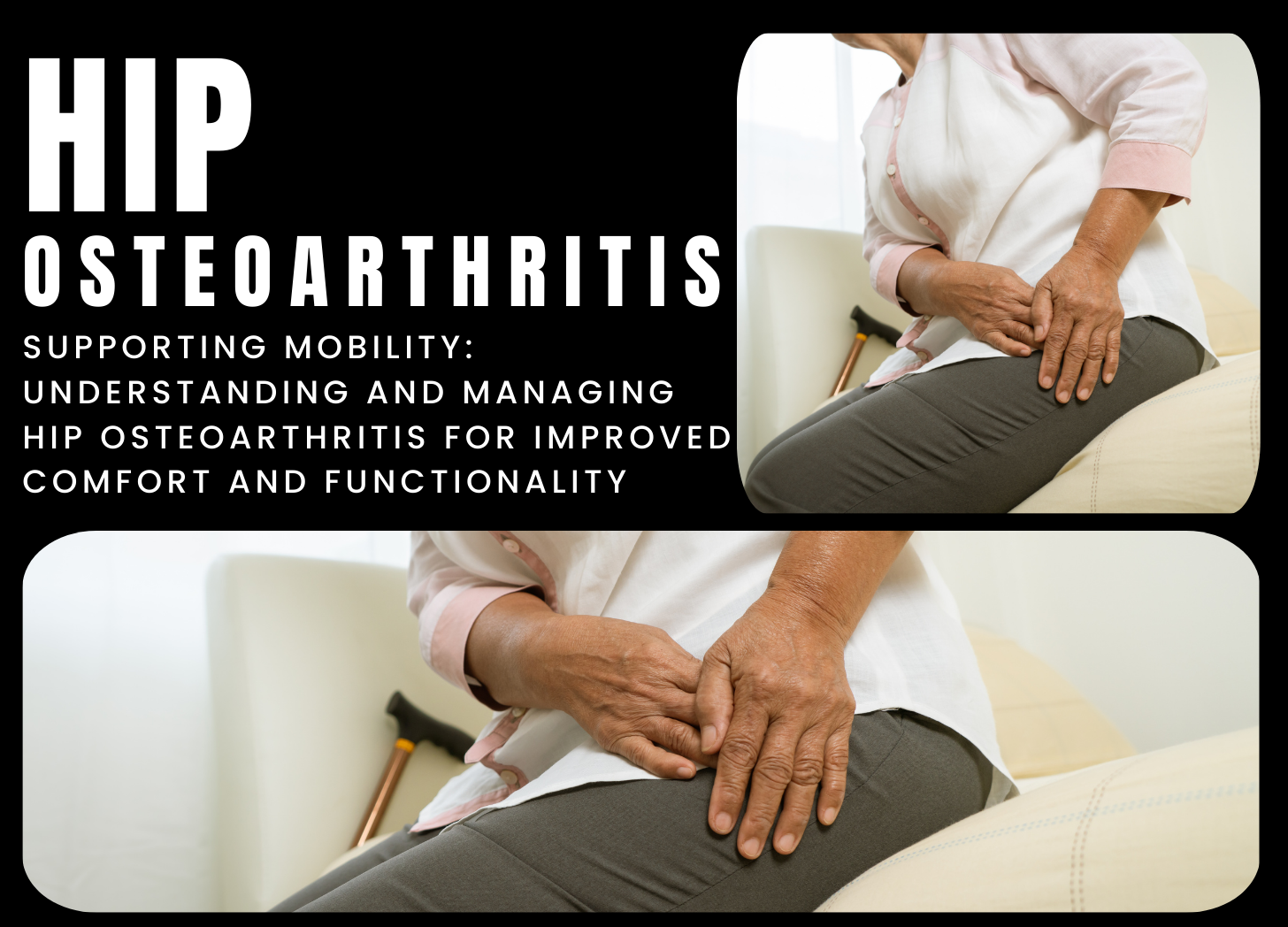
Hip osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint condition that affects the hip joint, causing cartilage degradation and bone deterioration. The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint, with the rounded head of the femur (thigh bone) fitting into the pelvis' acetabulum (socket). Cartilage covers the surfaces of the bones, cushioning them and allowing for smooth movement. However, with hip osteoarthritis, this cartilage wears down over time, resulting in discomfort, stiffness, and limited mobility. Although the actual etiology of hip osteoarthritis is unknown, it is thought to be a mix of variables…
READ MORE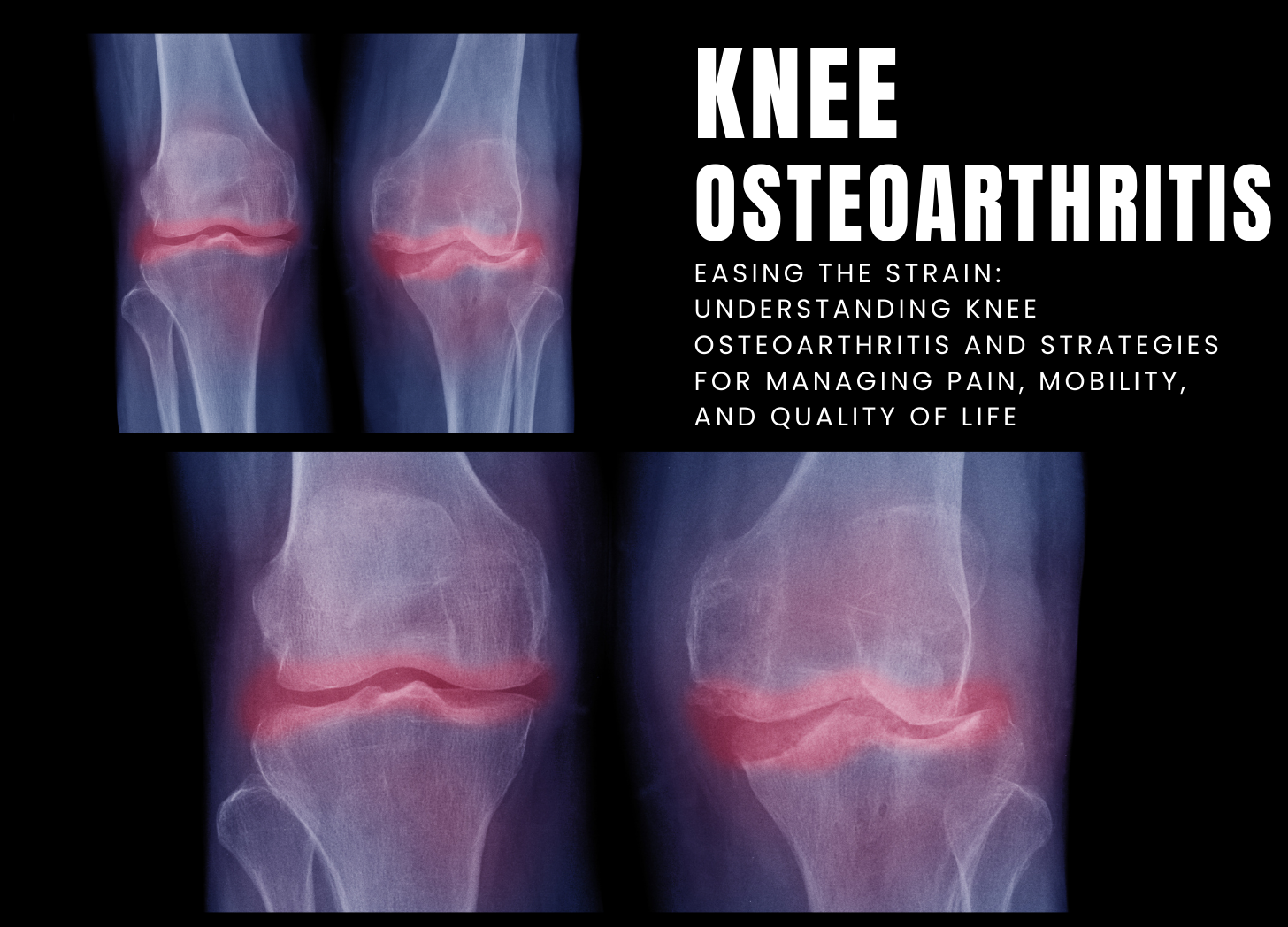
08 Apr 2024
Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is a common degenerative joint condition caused by the slow breakdown of cartilage in the knee joint, resulting in pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. Cartilage is a smooth, slippery tissue that cushions the ends of bones and allows for easy joint movement. As cartilage wears away, bones may rub against one another, resulting in pain, inflammation, and the production of bone spurs. Knee osteoarthritis can have a substantial influence on quality of life, limiting daily activities and reducing mobility. Although the specific etiology of knee osteoarthritis is…
READ MORE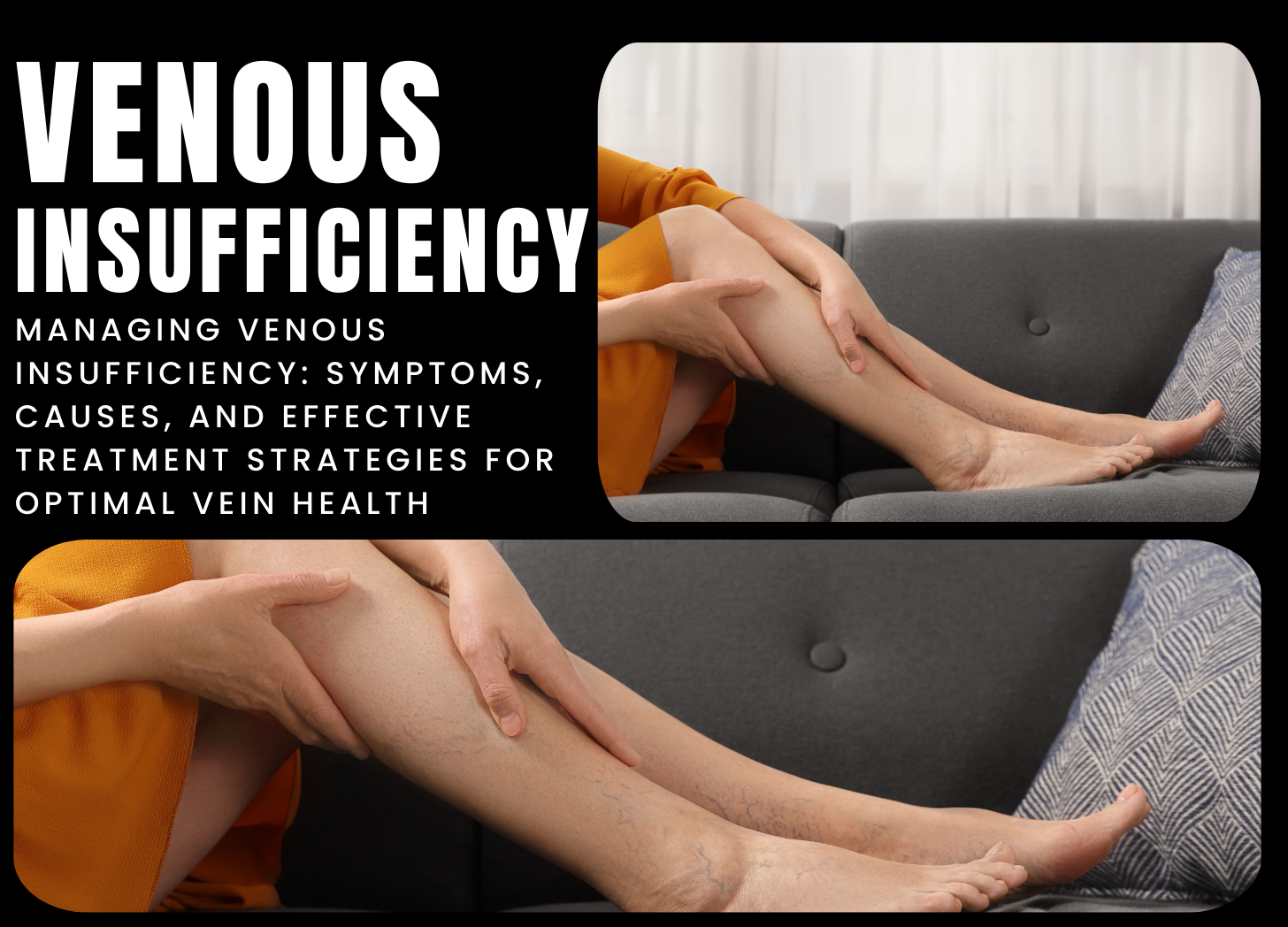
05 Apr 2024
Venous insufficiency is a disorder characterized by decreased venous function, mainly in the legs, which causes inadequate blood flow back to the heart. Normally, one-way valves in the veins prevent blood from flowing backward, allowing it to pass efficiently from the legs to the heart. However, when these valves are injured or weakened, blood can pool in the veins, causing swelling, pain, and changes in skin. Venous insufficiency can affect both superficial veins near the skin's surface and deep veins within the muscles of the legs. Chronic venous hypertension is…
READ MORE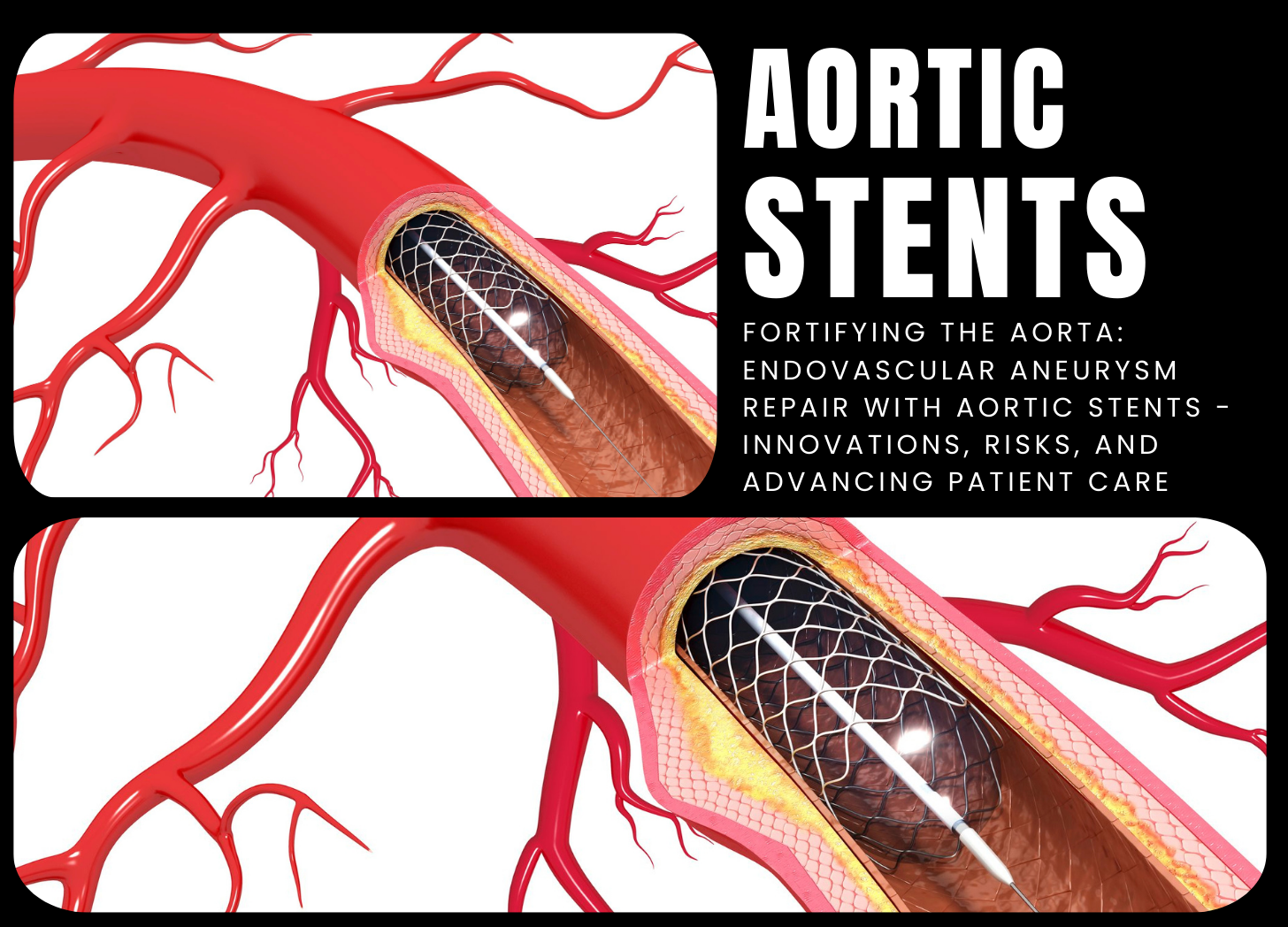
04 Apr 2024
Aortic stents, also known as aortic stent grafts or endovascular stent grafts, are medical devices used to treat aortic aneurysms and other problems of the aorta, the body's main artery. aorta aneurysms develop when a weakening portion of the aorta wall bulges or balloons outward, increasing the risk of rupture, internal bleeding, and other potentially fatal complications. Aortic stents are intended to strengthen and support the weakest part of the aorta, lowering the risk of rupture and restoring normal blood flow. An aortic stent is placed via a minimally invasive…
READ MORE
03 Apr 2024
Lymphoma is a cancer that develops in the lymphatic system, which is part of the immune system. The lymphatic system, which comprises lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, and bone marrow, is essential for battling infections and illnesses. Lymphoma develops when aberrant lymphocytes, a kind of white blood cell, grow uncontrollably, resulting in tumors in lymph nodes or other lymphatic tissues. Lymphoma is classified into two types: Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), which differ in histology, prognosis, and treatment. Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), commonly known as Hodgkin's disease, is distinguished by…
READ MORE
02 Apr 2024
Leukemia is a malignancy that affects the blood and bone marrow, resulting in an abnormal production of white blood cells. These abnormal white blood cells, known as leukemia cells, fail to function properly and crowd out good blood cells, reducing the body's capacity to fight infections and regulate bleeding. Leukemia is categorized into four forms based on the type of white blood cell involved: acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Each variety has unique characteristics in terms of onset,…
READ MORE
01 Apr 2024
Blood clots, also known as thrombi, are gel-like clumps of blood formed when blood components such as platelets and fibrin congeal to prevent bleeding at the site of a blood artery lesion. While blood clotting is a normal and necessary process for wound healing and preventing excessive bleeding, irregular clot development within blood vessels can cause major health problems. Blood clots can form in both arteries and veins and may be caused by a variety of underlying illnesses, lifestyle factors, or medical procedures. The most common types of blood clots…
READ MORE
29 Mar 2024
Hypothyroidism is a common endocrine condition defined by an underactive thyroid gland that produces insufficient thyroid hormones to meet the body's requirements. Thyroid hormones control metabolism, energy production, body temperature, heart rate, and other essential processes. Low thyroid hormone levels can cause a variety of symptoms and consequences impacting several organ systems. The most prevalent cause of hypothyroidism is autoimmune thyroiditis, also known as Hashimoto's thyroiditis, which occurs when the immune system erroneously assaults the thyroid gland, resulting in inflammation and damage. Other causes of hypothyroidism include thyroidectomy, radiation therapy…
READ MORE
28 Mar 2024
Acute bronchitis is a common respiratory illness marked by inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that transport air to the lungs. It is usually caused by viral infections, particularly those that cause the common cold or flu. Bacterial infections, exposure to irritants like tobacco smoke or air pollution, or inhalation of allergens can all cause acute bronchitis. Symptoms of bronchial tube inflammation include coughing, chest discomfort, and the production of mucus. Viral infections are the leading cause of acute bronchitis, accounting for the vast majority of cases. Respiratory viruses,…
READ MORE
27 Mar 2024
Upper respiratory infections (URIs) are widespread infectious illnesses that affect the nose, throat, sinuses, and upper airways. They are mostly caused by viruses, but bacteria can also play a role in some circumstances. URIs can range from mild to severe and include the common cold, sinusitis, pharyngitis (sore throat), and laryngitis. These illnesses spread via respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or speaks, or by touching contaminated surfaces. Upper respiratory infections are most commonly caused by viral pathogens such as rhinoviruses, influenza viruses, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV),…
READ MORE