Venous Insufficiency: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Venous insufficiency is a condition in which the veins, particularly in the legs, fail to efficiently return blood to the heart. This disorder occurs when the one-way valves in the veins become damaged or weakened, allowing blood to pool and causing various symptoms.
Causes
The primary cause of venous insufficiency is chronic venous hypertension, which increases pressure within the veins and stretches their walls. This pressure causes the vein valves to fail. Several factors can contribute to chronic venous hypertension, including:
- Extended Standing or Sitting: Prolonged periods in one position can strain the veins.
- Obesity: Excess weight increases pressure on the veins.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased blood volume during pregnancy can impact vein function.
- Aging: Aging veins may lose elasticity and function.
- Family History: Genetic predisposition to venous diseases.
- Previous Blood Clots: History of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can damage vein valves.
Symptoms
Venous insufficiency manifests through various symptoms, which may worsen with prolonged standing, sitting, hot weather, or hormonal changes. Common symptoms include:
- Swelling (Edema): Particularly in the legs and ankles.
- Aching or Heaviness: A sensation of weight in the legs.
- Cramping or Restlessness: Often felt in the legs.
- Itching or Tingling: Sensations that can accompany swelling.
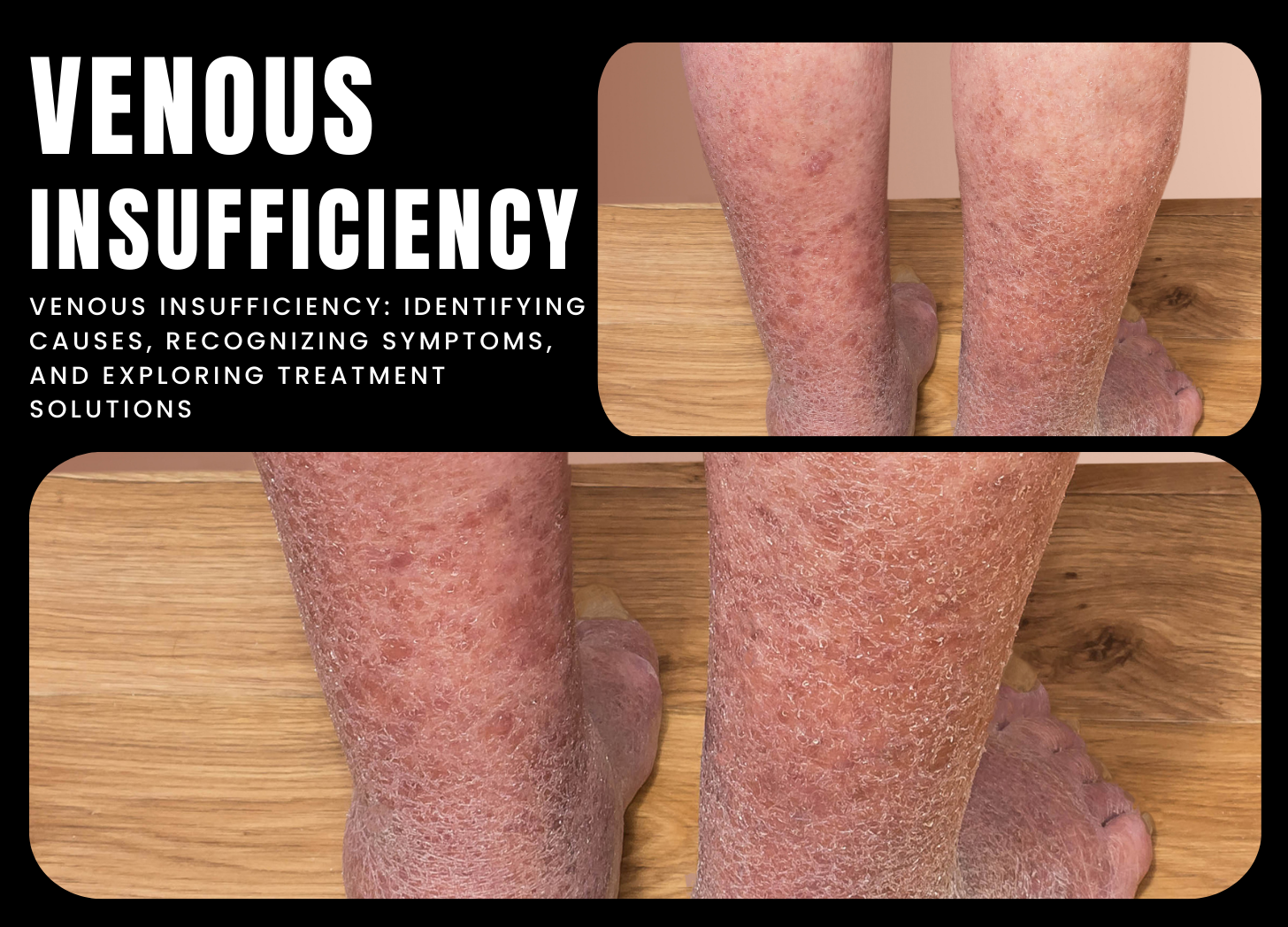
- Skin Changes: Discoloration or pigmentation changes.
- Varicose Veins: Enlarged, twisted veins visible beneath the skin.
- Venous Ulcers: Open sores that may develop on the legs or ankles.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing venous insufficiency involves a thorough medical history and physical examination, complemented by diagnostic tests. Techniques include:
- Venous Ultrasound (Doppler Ultrasound): Assesses blood flow and identifies abnormalities.
- Venography: An imaging procedure that uses contrast dye to visualize veins.
- Magnetic Resonance Venography (MRV): Provides detailed images of the veins.
Treatment
Management of venous insufficiency focuses on relieving symptoms, improving blood flow, and preventing complications such as ulcers or deep vein thrombosis. Treatment options include:
- Conservative Measures:
- Leg Elevation: Helps reduce swelling.
- Compression Stockings: Support vein function and minimize edema.
- Regular Exercise: Enhances muscle tone and circulation.
- Healthy Weight: Reduces pressure on the veins.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures:
- Endovenous Ablation: Uses heat to close off defective veins.
- Sclerotherapy: Involves injecting a solution to seal off problematic veins.
- Ambulatory Phlebectomy: Removes veins through small incisions.
Conclusion
Venous insufficiency is a common condition characterized by impaired vein function, leading to inadequate blood flow back to the heart. While it can cause discomfort and impact quality of life, early detection and appropriate treatment can manage symptoms effectively and prevent complications. Adopting lifestyle changes, using compression stockings, and seeking medical care as needed are crucial for managing venous health.
References
- Cleveland Clinic. (2022). Venous Insufficiency. Retrieved from Cleveland Clinic
- Society for Vascular Surgery. (2022). Venous Insufficiency. Retrieved from Society for Vascular Surgery
Post a Comment